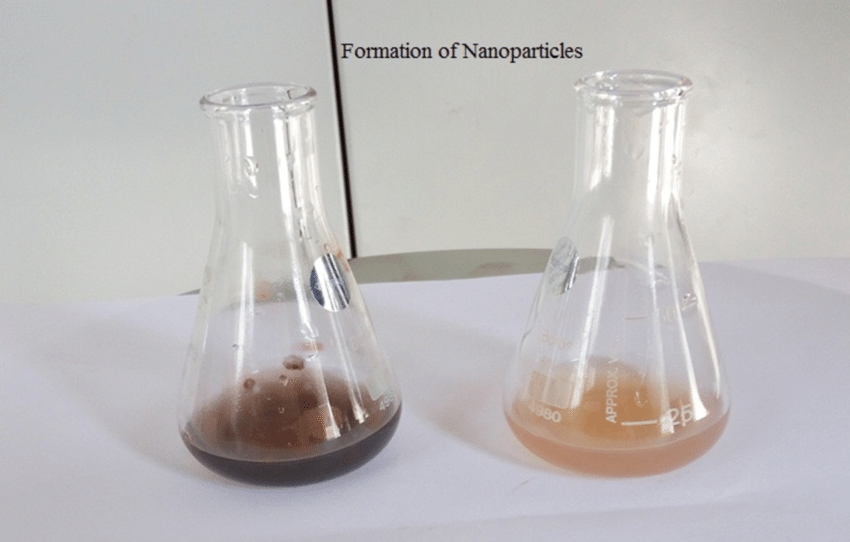
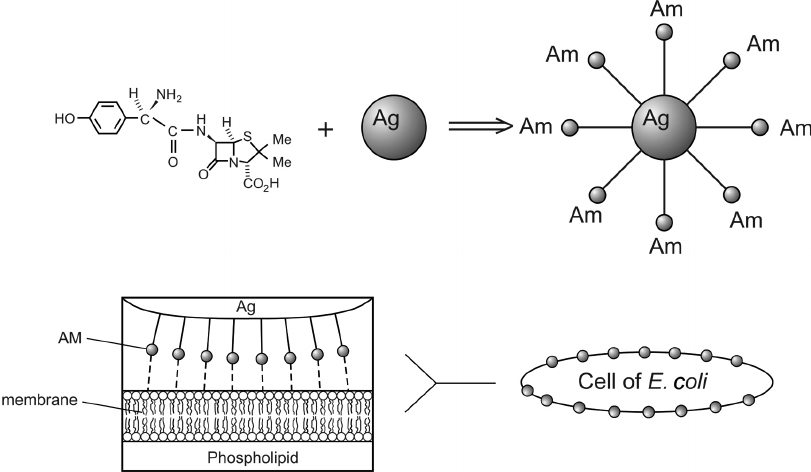
Product
Silver Nano Particles
Introduction
Silver nanoparticles are nanoscale-sized particles of silver, typically in the range of 1 to 100 nanometers, that exhibit unique physical and chemical properties due to their small size and high surface area-to-volume ratio. They have garnered significant attention for their versatile applications in various fields, including medicine, electronics, and catalysis, thanks to their antimicrobial, electrical, and optical properties.
-
Preparation using traditional method
Traditionally, silver nanoparticles are prepared using chemical reduction methods. The most common approach involves the reduction of silver ions (Ag+) by a reducing agent, such as sodium borohydride or citrate, in the presence of a stabilizing agent, such as polyvinylpyrrolidone (PVP). This method results in the formation of silver nanoparticles through a series of chemical reactions that reduce Ag+ ions to metallic silver, forming stable colloidal suspensions of nanoparticles.
-
Reaction
The reduction reaction involves the mixing of silver ions with the reducing agent and stabilizing agent under controlled conditions. The reducing agent donates electrons to the silver ions, causing them to aggregate and form nanoparticles. The stabilizing agent helps prevent the agglomeration of nanoparticles, maintaining their colloidal stability.
-
Disadvantages of traditional method
One major drawback of the traditional chemical reduction method is the use of toxic and hazardous chemicals. The reducing agents and stabilizing agents can be harmful to the environment and human health. Additionally, the process may require energy-intensive procedures and may result in the generation of chemical waste, making it less environmentally friendly.
-
Preparation using Green method
Green methods for the preparation of silver nanoparticles focus on eco-friendly and sustainable approaches. They often involve the use of plant extracts, microorganisms, or other biocompatible materials as reducing and stabilizing agents. These methods aim to reduce the environmental impact associated with the synthesis of nanoparticles.
-
Reaction
In green synthesis, plant extracts or microorganisms are used to reduce silver ions and stabilize the resulting nanoparticles. The bioactive compounds in the plant extracts or microorganisms play a key role in the reduction process. The reaction is carried out under milder conditions, avoiding the use of hazardous chemicals. Green methods are advantageous because they are more environmentally friendly and biocompatible.
-
Advantages of Green method
The primary advantage of green synthesis methods is their sustainability and reduced environmental impact. They eliminate the need for toxic chemicals and energy-intensive processes. Green methods are also cost-effective and often result in highly stable silver nanoparticles with potential biomedical and environmental applications. Furthermore, these methods can be easily scaled up for commercial production.
-
Applications
Silver nanoparticles find diverse applications in various fields. They are used in medicine for wound healing, drug delivery, and as antimicrobial agents. In electronics, they serve as conductive inks, enhancing the performance of electronic devices. In the field of catalysis, they act as efficient catalysts for various chemical reactions. Their antimicrobial properties make them valuable in the development of antibacterial coatings for surfaces. Moreover, they are used in water purification and as a component in sensors and diagnostic devices due to their unique optical properties.