Product
Nylon-6,6
Introduction
Nylon-6,6, a type of polyamide, is a versatile and widely used synthetic polymer. It derives its name from the fact that it contains six carbon atoms in each of its amide groups. This high-performance material is known for its exceptional strength, durability, and resistance to abrasion, making it a favored choice for various industrial and consumer applications.
-
Preparation using traditional method
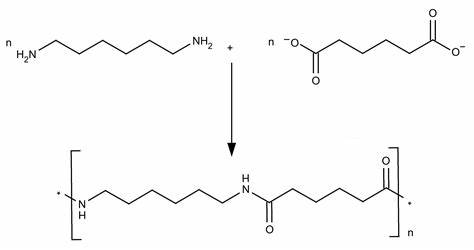
The traditional method for synthesizing Nylon-6,6 involves a two-step process. First, adipic acid and hexamethylenediamine are reacted in the presence of a catalyst, typically sulfuric acid, to produce a polymer intermediate. This intermediate is then subjected to a polycondensation reaction at high temperatures to form Nylon-6,6.
-
Reaction
In the first step, adipic acid and hexamethylenediamine react to form a salt, and water is produced as a byproduct. The salt is then converted into the polymer by heating and further condensation reactions, leading to the formation of Nylon-6,6 with repeating amide linkages.
-
Disadvantages of traditional method
One of the major disadvantages of the traditional method for Nylon-6,6 synthesis is the production of substantial amounts of hazardous waste, including water, which requires proper disposal. Additionally, the process relies on non-renewable resources and can be energy-intensive, contributing to environmental concerns.
-
Preparation using Green method
An eco-friendly approach to Nylon-6,6 production involves using renewable resources and environmentally friendly processes. For instance, bio-based adipic acid derived from biomass and renewable hexamethylenediamine sources can be used to produce Nylon-6,6 in a more sustainable manner.
-
Reaction
The green method for Nylon-6,6 synthesis utilizes bio-based adipic acid and hexamethylenediamine, reducing the environmental impact. The reaction proceeds similarly to the traditional method, but the starting materials are derived from sustainable sources, which lessens the carbon footprint.
-
Advantages of Green method
The primary advantage of the green method is its reduced environmental impact. By replacing petroleum-based precursors with renewable alternatives, the process minimizes greenhouse gas emissions and waste production. This approach aligns with sustainability goals and promotes a more eco-conscious production of Nylon-6,6.
-
Applications
Nylon-6,6, whether produced traditionally or using a green method, finds extensive applications across various industries. Its exceptional mechanical properties, including high tensile strength and resistance to wear, make it ideal for use in automotive parts, textiles, carpets, and engineering plastics. It is also utilized in medical devices, packaging materials, and even clothing, where its durability and flexibility are highly valued. In summary, Nylon-6,6 remains a crucial material in modern manufacturing, with the potential for greener and more sustainable production methods.