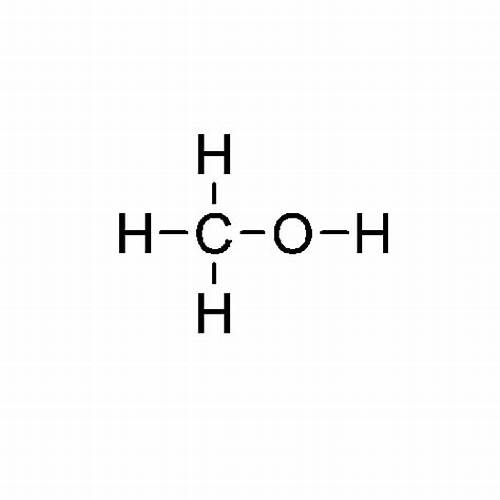
Product
Methanol
Introduction
Methanol, also known as methyl alcohol or wood alcohol, is a simple organic compound with the chemical formula CH3OH. It is a colorless, flammable liquid with a slightly sweet odor. Methanol is a crucial industrial chemical used primarily as a solvent, antifreeze, and as a raw material in the production of various chemicals.
-
Preparation using traditional method
Traditionally, methanol is prepared through a process called destructive distillation, where wood or other organic materials are heated in the absence of air, producing methanol as one of the products. This method has been largely replaced by more efficient and environmentally friendly processes. The reaction involved in traditional methanol production is the pyrolysis of wood or organic material, which generates a mixture of volatile compounds, including methanol.
-
Disadvantages of traditional method
The disadvantage of the traditional method of methanol preparation is that it is energy-intensive, requires large amounts of wood or organic feedstock, and can result in environmental issues due to the release of harmful byproducts and deforestation.
-
Preparation using Green method
Green methods for methanol production involve the catalytic conversion of carbon dioxide and hydrogen, usually derived from natural gas or other sources, into methanol. This method not only utilizes carbon dioxide as a feedstock but also reduces the carbon footprint of methanol production. The reaction for green methanol production is a catalytic hydrogenation process that converts CO2 and H2 into methanol, typically using copper-based catalysts.
-
Advantages of Green method
The advantage of the green method is that it provides a more sustainable and environmentally friendly approach to methanol production, reducing greenhouse gas emissions and dependence on fossil fuels.
-
Applications
Methanol is used in various applications, including as a fuel, antifreeze, and as a feedstock in the production of chemicals such as formaldehyde, acetic acid, and methyl tert-butyl ether. It is also utilized in the pharmaceutical and chemical industries and as a fuel additive to enhance combustion efficiency and reduce emissions in internal combustion engines.