Product
Carbon Nano tubes
Introduction
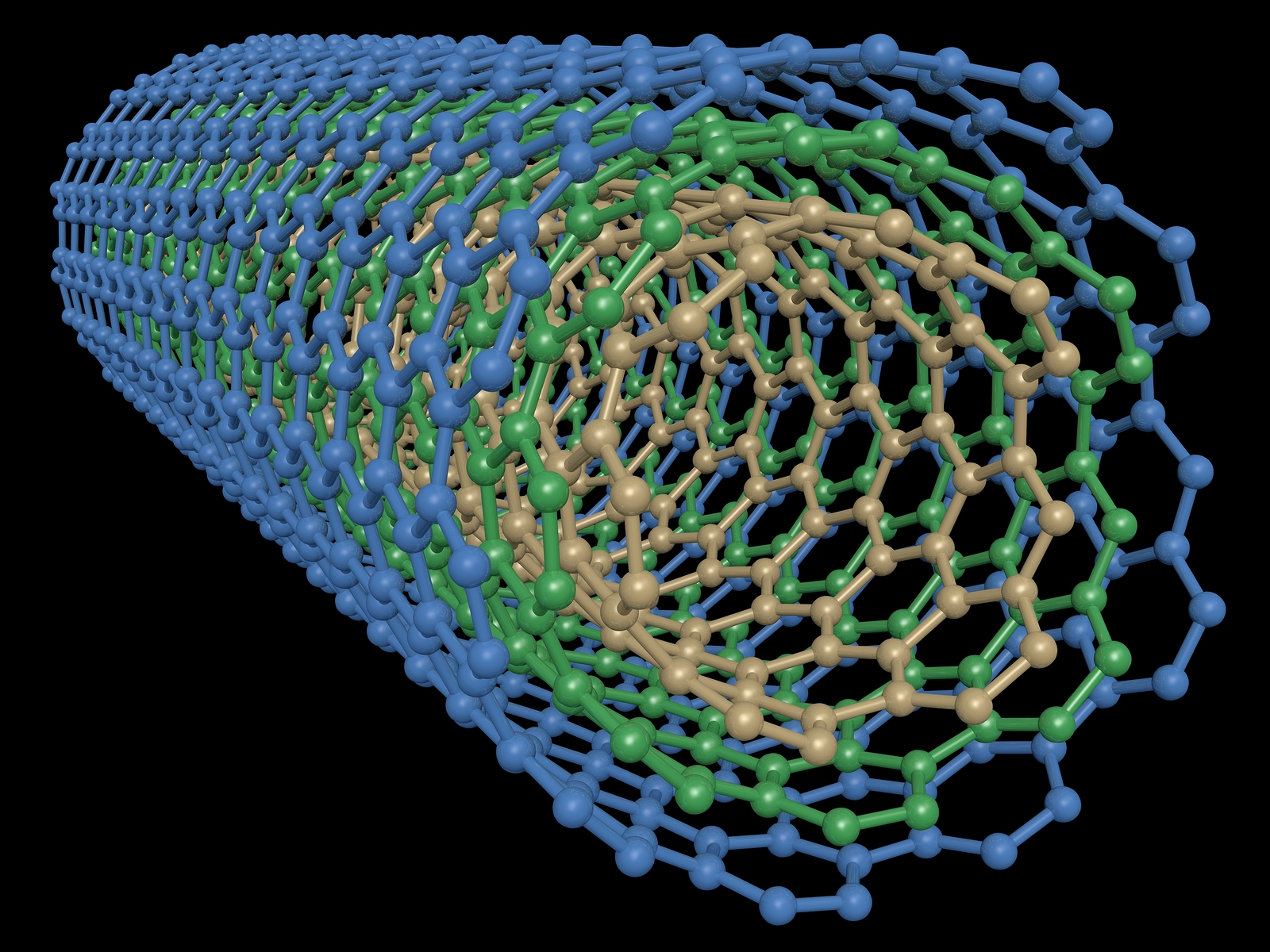
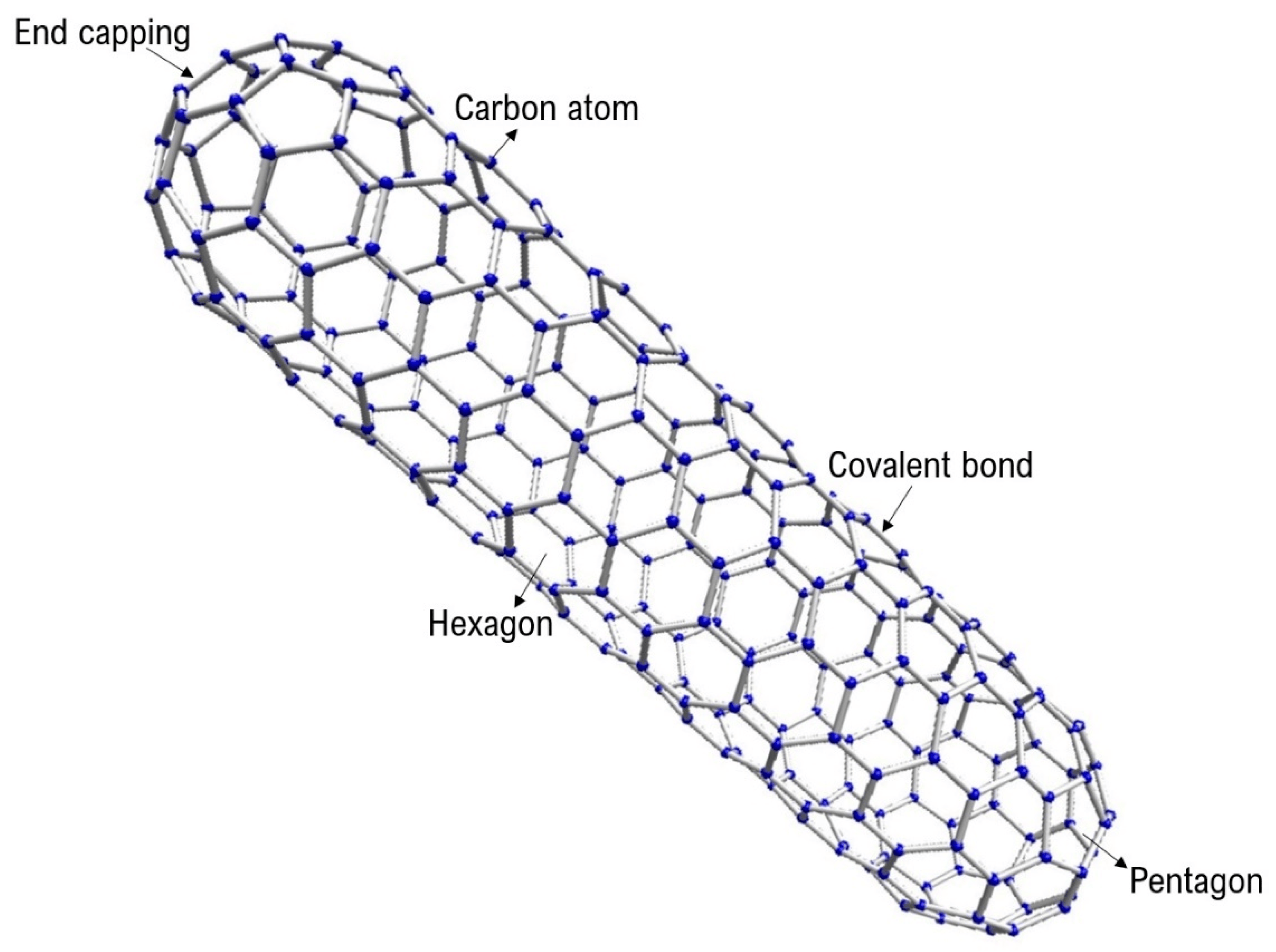
Carbon nanotubes (CNTs) are cylindrical nanostructures composed of carbon atoms arranged in a hexagonal lattice. These remarkable materials have unique electronic, mechanical, and thermal properties, making them the focus of extensive research and potential applications in various fields.
-
Preparation using traditional method
Preparation using traditional methods involves techniques like chemical vapor deposition (CVD) and arc discharge, where carbon atoms are condensed into nanotubes through high-temperature reactions. In CVD, a carbon-containing precursor gas is heated to deposit carbon onto a catalyst surface, forming nanotubes.
-
Disadvantages of traditional method
One major disadvantage of traditional CNT preparation methods is the high energy consumption and the production of toxic byproducts. These methods also require the use of metal catalysts, which can contaminate the CNTs and hinder their application in some fields.
-
Preparation using Green method
Preparation using green methods aims to address these issues by employing more environmentally friendly processes. One such approach involves the use of naturally derived carbon sources like biomass or waste materials, reducing the environmental impact.
-
Advantages of Green method
In green CNT synthesis, researchers use renewable carbon sources in a controlled environment, promoting carbon nanotube growth without the need for toxic catalysts. This method has the advantage of being more sustainable and eco-friendly, with reduced energy consumption and less pollution.
-
Applications
Carbon nanotubes have a wide range of applications, including nanocomposites for lightweight, strong materials, conductive additives for electronics, drug delivery vehicles in medicine, and as sensors for various gases and molecules. The development of green synthesis methods for CNTs not only enhances their properties but also supports more sustainable and responsible manufacturing practices for these versatile nanomaterials.