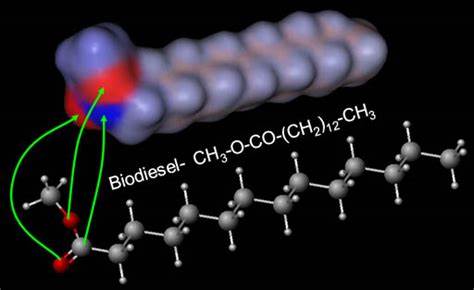
Product
Biodiesel
Introduction
Biodiesel is a renewable and environmentally friendly alternative to traditional fossil fuels. It is typically produced from various feedstocks, with vegetable oils and animal fats being the most common sources. Biodiesel is created through a chemical process known as transesterification, which converts these feedstocks into a fuel suitable for diesel engines.
-
Preparation using traditional method
The preparation of biodiesel using the traditional method involves the reaction of a vegetable oil or animal fat with an alcohol, typically methanol or ethanol, in the presence of a catalyst, such as sodium hydroxide or potassium hydroxide. This process results in the production of biodiesel and glycerol as a byproduct.
-
Disadvantages of traditional method
However, there are several disadvantages associated with the traditional method of biodiesel production. It can generate large amounts of waste glycerol, and the use of methanol, as well as strong alkali catalysts, can have negative environmental impacts. Additionally, feedstock availability and competition with food production are concerns associated with traditional biodiesel production.
-
Preparation using Green method
In contrast, the green method of biodiesel production aims to address these issues. This approach often involves the use of non-food feedstocks, like algae or waste cooking oils, and uses more sustainable and environmentally friendly catalysts. The transesterification reaction in the green method is typically carried out at lower temperatures and pressures, reducing energy consumption and greenhouse gas emissions.
-
Advantages of Green method
The advantages of the green method include reduced waste generation, a smaller environmental footprint, and a potential to use locally sourced and sustainable feedstocks. This method aligns more closely with the principles of a circular and green economy, promoting a cleaner and more sustainable energy source.
-
Applications
Biodiesel has various applications, primarily as a substitute for conventional diesel fuel in transportation, such as cars, trucks, and buses. It can also be used as a heating oil or as a component in aviation fuel. Biodiesel's potential applications are expanding, particularly as the world seeks cleaner and more sustainable energy sources to combat climate change and reduce dependence on fossil fuels.