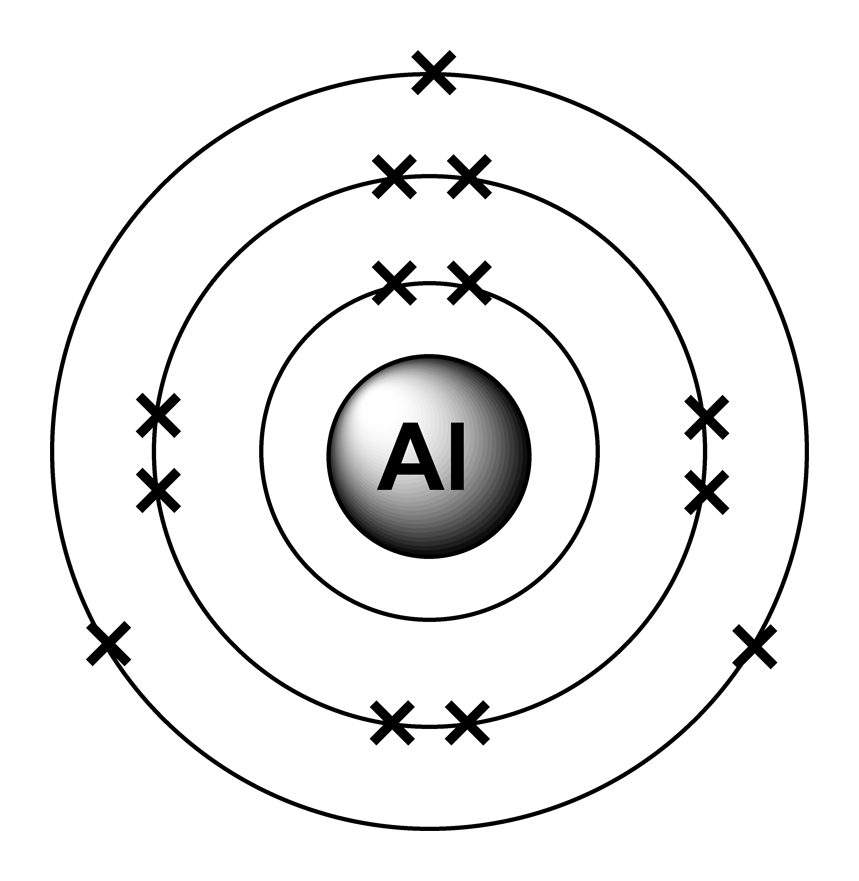
Product
Aluminium
Introduction
Aluminium is a versatile chemical element with the symbol Al and atomic number 13. It is a lightweight and abundant metal that is known for its excellent conductivity, corrosion resistance, and widespread use in various industrial applications.
-
Preparation using traditional method
Aluminium is typically produced using the Hall-Héroult process, a traditional method involving the electrolysis of alumina (Al2O3) in molten cryolite (Na3AlF6). This process consumes a significant amount of energy, primarily from fossil fuels, making it energy-intensive and environmentally challenging.
-
Reaction
In the Hall-Héroult process, alumina is dissolved in molten cryolite, and an electric current is passed through the solution. This causes the reduction of alumina to aluminium metal at the cathode, with oxygen gas evolving at the anode. The molten aluminium is then collected and further processed.
-
Disadvantages of traditional method
The traditional method of aluminium production is energy-intensive, relies on non-renewable energy sources, and generates a substantial carbon footprint due to greenhouse gas emissions. It also requires the extraction of bauxite ore, which can have detrimental environmental impacts.
-
Preparation using Green method
Green methods for aluminium production involve more sustainable and energy-efficient processes. One such method is the electrolysis of aluminium chloride (AlCl3) in ionic liquids or room-temperature molten salts, which reduces energy consumption and environmental impact.
-
Reaction
In green methods, aluminium chloride is electrolyzed at lower temperatures using ionic liquids or molten salts, which require less energy compared to the Hall-Héroult process. This results in the deposition of aluminium metal at the cathode.
-
Advantages of Green method
Green methods for aluminium production are more energy-efficient, have a reduced carbon footprint, and can potentially use renewable energy sources. They also avoid the need for cryolite and bauxite, reducing the environmental impact of mining and refining processes.
-
Applications
Aluminium, prepared through either traditional or green methods, finds extensive use in industries such as aerospace, automotive, construction, packaging, and electronics. Its properties of low density, excellent electrical conductivity, and corrosion resistance make it an ideal choice for a wide range of applications, including aircraft, automobiles, structural components, cans, and electrical wiring. Additionally, aluminium alloys offer improved strength and versatility, further expanding their applications across various sectors.